PUT
The PUT packet is used to append data to a bucket or modify existing data in a bucket.
Request
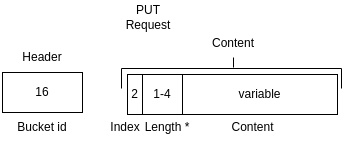
Figure A: PUT request byte-map (header and body)
The PUT request (see Figure A) includes a header. This header contains one field: the bucket id and is used to indicate which bucket is used.
The PUT packet accepts no extra flags.
The body contains an array with the following fields:
- Slot index: a 2-byte integer (uint-16) that indicates the index of the slot in the bucket that must be replaced. If you want to use the first empty slot, try an APPEND request instead.
- Length: a dynamically sized integer that indicates the length of the following content.
- Content: variable-length byte content. Can be literally everything, but is limited to ~268 MB due to the dynamic length property of the request packet which is currently limited to 4 bytes from which 28 bits can be used.
The indicated slot index will replace the data in the slot if it is already in use and you have write permissions. If you have append permissions and you try to write data to a slot that is not empty or is not the next empty slot in the bucket the server will send error code 51.
Response
Figure B: PUT response byte-map
The PUT response is empty.
You might encounter the following error codes:
- 3 (invalid permissions): you try to put data on a non-empty slot without write permissions or you have no write or append permissions at all. This can also mean you are missing the bucket key.
- 4 (authentication failed): the bucket key you are providing might not be valid
- 5 (payload too large): you try to put more data to a slot than the server supports. Try splitting your data on multiple slots
- 21 (bucket does not exist): The bucket you are trying to PUT to does not exist
- 51 (selected index taken): Selected index in bucket is already taken (only thrown if no write permissions, else the index is overwritten)
Process and flow
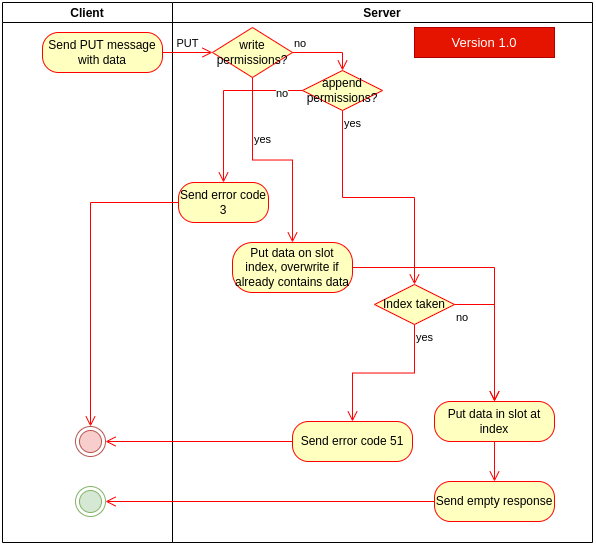
Figure C: PUT process flow
The PUT process (see Figure C) goes as follows:
- The client sends a PUT message containing the data and optionally containing a slot index
- The server checks if the user has permission to modify the bucket. If not, error code 3 is sent
- If the user has write permissions, put data to that slot (overwrite if slot is already in use)
- If the user has append permissions, only put data to that slot if slot is not already filled and is the first following empty slot in the bucket. If not the first following empty slot, return error 3. If the slot is already taken, return error 51.
← Back to Home - To Transport - Prev: CREATE packet - Next: APPEND packet →